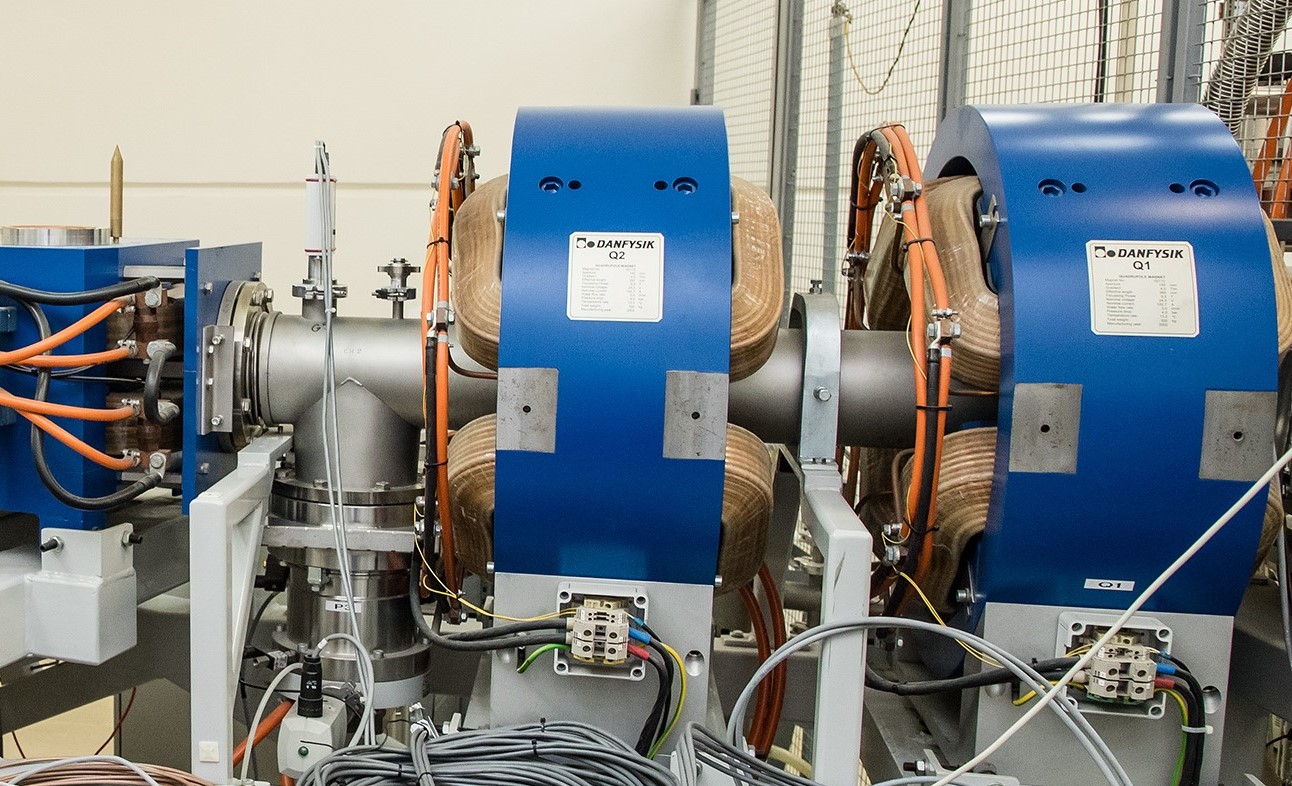
The Isotope Separation OnLine (ISOL) method is widely used in mass analysis for determination of short-lived isotopes. It is based on cooling and stopping the reaction products, making possible their magneto-optic and electrostatic analysis, as well as their separation from the primary beam in the non-interruptible “online” mode. The experiment aimed at studying a new carbon nanomaterials application was performed on the U-400M heavy ion beam at MASHA facility, FLNR, JINR. The main goal of the experiment was to determine the radiation resistance of these materials for the ISOL method. The previous experimental research performed with a thermally expanded graphite heat catcher showed incompatibility with high intensity beams. The improvements made to the ISOL method application allow synthesizing new products at the beam intensities of up to 0.5 pµA and higher for the SHE factory perspective.
Tasks
- perform the analysis of the ISOL (Isotope Separation OnLine) method using experimental data of gathering volatile products
- identify the weak and strong points of the solid ISOL method
- propose an upgrade version for MASHA installation.
Preliminary schedule by topics/tasks
1. Introduction lecture
2. Main parts overview + literature observation
3. Experimental data gathering
4. Data analysis using OriginPro software and chart of nuclides
5. Discussion of the results with the supervisor
6. Preparation of the final report.
Required skills
- principles of nuclear reactions
- conservation of energy, mass, momentum, and charge laws
- principles of magnetic mass-spectrometry
- interaction of radiation with matter physics
Acquired skills and experience
- advanced knowledge in acceleration technology
- parts used at MASHA installation
- mass-to-charge spectrometry
- principles, advantages, and limitations of the solid ISOL method widely used at nuclear reaction mass-spectrometry
Recommended literature
1. Chemical identification of Dubnium as a decay product of element 115 produced in the reaction 48Ca + 243Am. S.N. Dmitriev, Yu.Ts. Oganessyan, V.K. Utyonkov et al. Dubnium as a decay product.
2. Chemical characterization of element 112. R. Eichler, N. V. Aksenov, A. V. Belozerov et al. Nature. Letters. Vol. 447, May 2007.
3. The current status of MASHA setup. V. Yu. Vedeneev, A.M. Rodin, L.Krupa. Hyperfine Interactions 238:19 (2017).
4. Separation efficiency of the MASHA facility for short-lived mercury isotopes. A.M. Rodin, A.V. Belozerov, E.V. Chernysheva. Hyperfine Interactions. 227:209-221 (2014).
5. MASHA Separator on the Heavy Ion Beam for Determining Masses and Nuclear Physical Properties of Isotopes of Heavy and Superheavy Elements. A.M. Rodin, A.V. Belozerov, D.V. Vanin. Instruments and Experimental Techniques, 2014, Vol. 57, No. 4, pp. 386–393. © Pleiades Publishing, Ltd., 2014.